Podcast: Play in new window | Download (Duration: 1:17:36 — 71.1MB)
Season 2019 / 2020 – Talk 12 – The Great Depression
In The Great Depression Andrew Cole tells us about the period between 1929 and 1939. Whilst much of his talk is about the US he also tells us about the global context.
Please note: this talk is from early March 2020 and is therefore from before the effects of the Coronavirus pandemic fully hit economies.
What was The Great Depression?
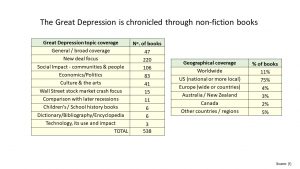
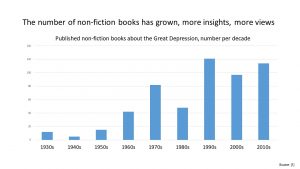
We learn that a great deal has been written about this period. There are over 500 non-fiction books, 100+ television documentaries and at least 5,000 papers. Add to that 11,000+ YouTube videos and 24.4 million hits on Google!
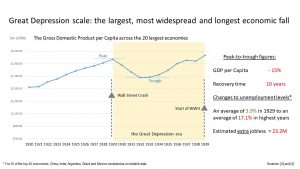
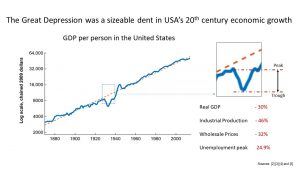
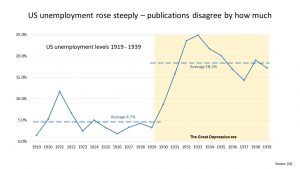
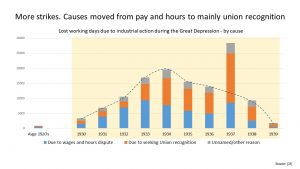
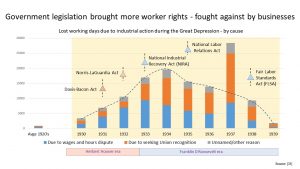
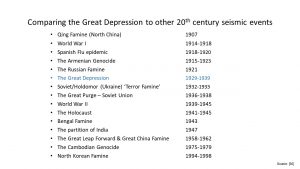
It is described as ‘the longest and most severe economic downturn in the history of the industrialised world’. The result – widespread long-term unemployment, hardship and unrest.
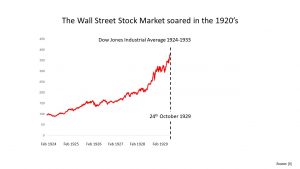
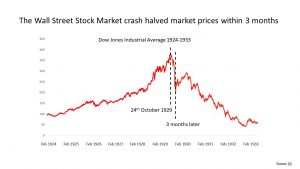
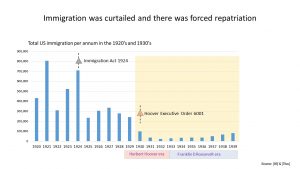
It covers the period from the Wall Street Crash (24th October 1929 – ‘Black Thursday’) to the start of World War Two (1st September 1939).
Causes:
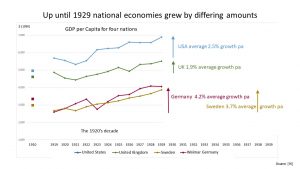
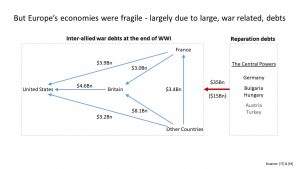
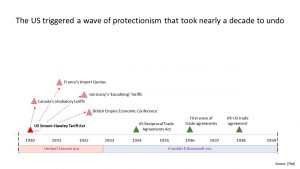
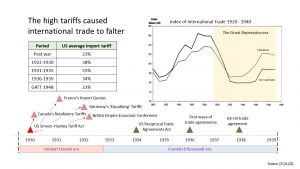
The European economies were fragile. The First World War had been very expensive. The losers, the Central Powers (Germany, Bulgaria, Austria, Hungary and Turkey), had the added burden of reparations.
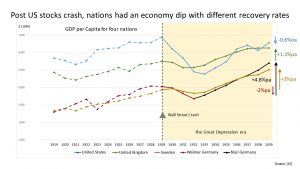
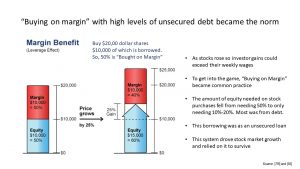
In the US people believed that the stock market would continue rising. In the US many shares were bought using loans. Some of the financial institutions used sharp practices.
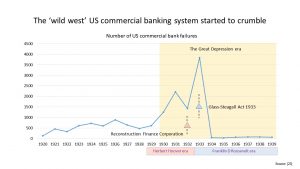
When the market crashed loans were called in resulting in bankruptcies and there were also bank failures. This then affected industry and resulted in lower wages and unemployment.
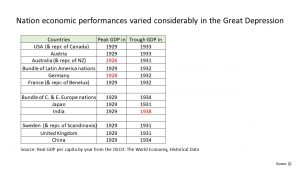
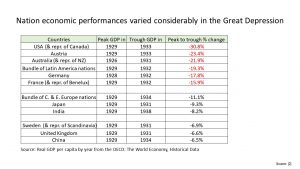
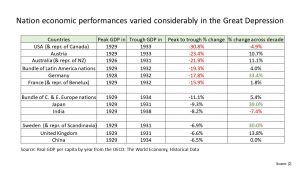
This reverberated around the world and there was a global recession.
Remedies:
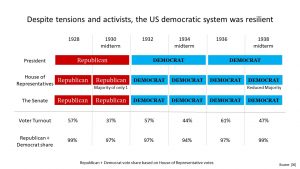
Three US Presidents were in power during the period leading up to and through the depression:
- Calvin Coolidge. President from August 1923 to March 1929. Presided over much of the ‘roaring Twenties’.
- Herbert Hoover. President from March 1929 to March 1933. The Peak to Trough era.
- Franklin D Roosevelt. President from March 1933 to April 1945. The ‘New Deal’ era and World War II.
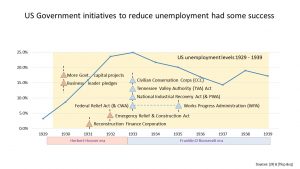
The US Governments tried a number of stimulus packages. Many of Hoover’s were unsuccessful whereas Roosevelt’s New Deal were more successful. The Roosevelt era also saw the 1933 Homeowner’s Refinancing Act and the 1935 Social Security Act.
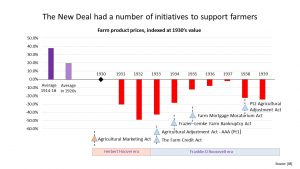
The New Deal also had measures to help farmers who had been hit by both Bank failures and the dust storms cause by over cropping.
The Consequences:
Many consequences of The Great Depression have been suggested, amongst them are:
- The rise of Hitler and World War II
- A change in public attitudes to risk taking.
- A greater understanding for the need for regulation although many might question its effectiveness.
- The role of Governments and Central Banks.
Hear the whole story by listening to this podcast.
Please note: Some of the views expressed and expressions used in this talk reflect views common during this period of history and do not reflect those of the speaker, Farnham U3A World History Group or The MrT Podcast Studio.
To view the photographs accompanying this talk:
These graphics are from the talk. For copyright reasons some of the photographs, recordings, newspaper headlines and cartoons used in the original talk have had to be omitted.
Please click on a thumbnail to open the gallery:
References:
The list of References for further reading is here.
About this podcast:
The Farnham U3A site is found here.
This podcast is also available through the Amazon Music, Apple Podcasts, Castbox, Deezer, Podchaser, Spotify and Stitcher ‘apps’.
AKM Music has licensed Media Magazine for use as the title music.
© The MrT Podcast Studio and Farnham U3A World History Group 2020
![]()